
The gravity of the threat of entry depends on the current barriers to entry and the reaction from existing competitors that the entrants can expect. Sometimes this might cause a shakeup in the industry, especially from those entrants who have enormous resources. Furthermore, new entries to an industry often bring new capacity and the desire to gain market share, and often with substantial resources.

At the same time, incumbents typically have to spend more to satisfy their customers. It caps prices because higher industry prices would make entry more attractive to newcomers. The threat of entry dampens profitability in two ways. In the following paragraphs, I will explain each of the five forces in detail. The general rule is “the more powerful the forces, the more stress it puts on prices and costs”.

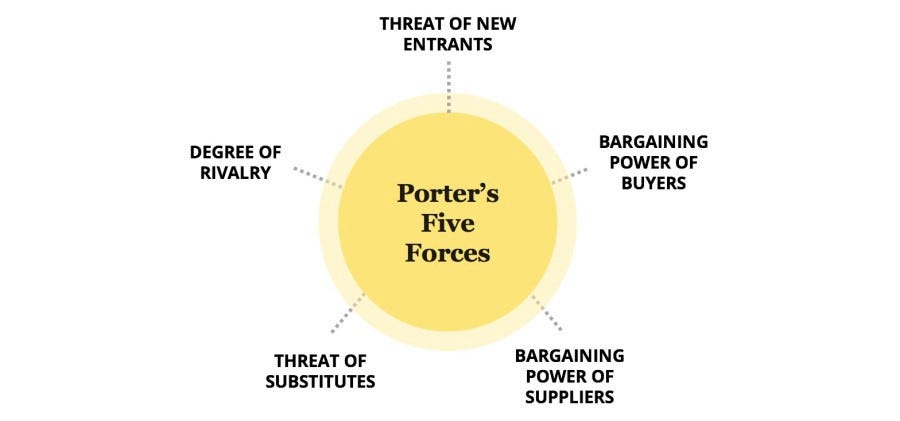
The real point of the competition is not to beat your rivals, but to earn profits. Strategy Formulation with Porter’s Five Forces By understanding each of Porter’s five key forces in a particular industry, strategists can identify what strengths or weaknesses can be exploited to strengthen the position of the organization. The five forces are namely: (1) Threat of entry (2) Threat of substitutes (3) Rivalry among existing competitors (4) Power of suppliers (5) Power of buyers. So, what are porter’s five forces? By simple definition, porter’s five forces model is an analysis tool that uses five industry forces to determine the intensity of competition in an industry and its profitability level. Strategy consultants often use Porter’s five forces as the framework or starting point, when making an evaluation of a firm’s strategic position. Lee Bin wrote this essay in Module 4 and has since completed all five modules of the Valuation Master Class.įor every organization, it is the utmost importance for strategists to enhance long-term profits. Switching cost: Switching costs are the costs associated with a customer transitioning from one company to another and can deter buyers from choosing a new company due to the additional expense.This is a Valuation Master Class student essay by Lim Lee Bin from May 20, 2018.

Retaliation: Existing companies in the industry sometimes resist and deter new entrants from entering their competition. Government regulations: Government and regulatory requirements may limit how a company can conduct business and require permits or licenses for entry into the industry. Access to suppliers and distribution channels: New entrants may struggle to find access to suppliers and distribution channels since many already provide service to existing companies.īarriers to exit: When a company can't easily leave the competition due to factors such as high exit costs, new entrants may be hesitant to join the environment in case their business doesn't succeed.īrand loyalty: If an industry consists of companies with high levels of brand loyalty, it can be challenging to enter the competition.Ĭapital requirement: Certain industries have high capital costs, making entry limited to those who have the necessary resources.Ĭost advantages: Companies that currently exist in the industry can sell their products or services at a price lower than new entrants.ĭifferentiated products: If a new entrant plans to sell a product that's highly differentiated by the current company, they may have to come up with unique, new features in order to compete.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
